Biofouling composition includes organisms ranging from bacteria, algae, and barnacles in a marine environment where noticeable aquatic growth appears on ships and underwater structures. Biofouling increases ship hull drag, corrosion, fuel consumption, and engine stress.
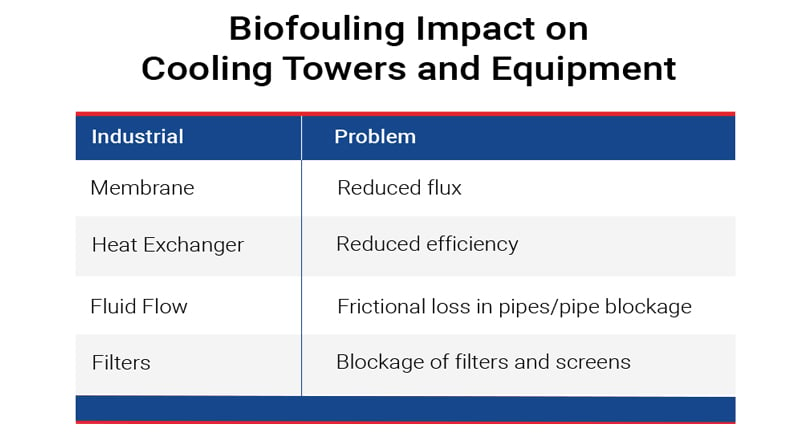
Industrial biofouling occurs in areas such as power plants, water treatment systems, and food/beverage industries. Problems include pipe blockage, decreased membrane flux, contaminated water, and reduced heat-exchanger efficiency.
Controlling biofouling is accomplished through a variety of ways. In this article, we discuss biofouling management, its impact on industrial cooling towers, biofouling's effect on people and the environment, and the benefits of using an epoxy coating system to protect against chemical and atmospheric corrosion.
Chapters
1. Market Overview and Industrial Biofouling Management
Projections indicate the cooling tower market to reach USD 2.87 billion by this year, at a CAGR of 4.2% from 2015 to 2020. A cooling tower is used in various applications, such as chemical, petrochemical and oil & gas, HVACR, food & beverage, and power generation.
Cooling towers are essential in most industrial processes. However, there is a need to control biofouling in cooling systems. Cooling towers require proper maintenance to ensure the most efficient operation and to reduce downtime. There are several cooling tower challenges: water conservation, corrosion, scale, deposits, and microbiological activity.
Learn the fundamentals of How Cooling Tower Systems Work
2. Biofouling in Industrial Water Systems (cooling towers and equipment)

Image by cwizner from Pixabay
Cooling tower systems provide cooling in industrial and commercial applications. The key components include:
- Cooling tower
- Recirculating pump
- Heat exchanger
Cooling towers vary in size and design but are used for one function, to extract the heat through the evaporation of water. The towers require proper maintenance to ensure the most efficient operation and to reduce downtime.
Cooling towers are systems prone to the nature of their actions and environment. Because of this, they encounter several cooling tower challenges: microbiological fouling, controlling corrosion, and scaling as in deposit formation.
Microbiological activity /Biological growth
A cooling tower's primary function is to lower water temperatures. The water is recycled to optimize water utilization. Meaning cooled water is collected at the bottom of the tower and pumped back into the tower.
However,
Because the towers contain large amounts of water, they are a breeding ground for bacteria. A biofilm of bacteria, fungi, and algae can establish itself and rapidly grow on the wet surfaces of the cooling tower. Industrial cooling tower systems can present an ideal environment for the growth of Legionella pneumophila, a bacterium found in untreated freshwater worldwide.
Professional water treatment minimizes these challenges. Chem-Aqua is an industry leader in providing custom water treatment solutions for a variety of applications and industries. They specialize in providing custom-designed water treatment programs for boiler, cooling, and process water systems.
Corrosion
There are different types of corrosion in cooling tower systems including, pitting, microbiologically influenced, and erosion. The corrosion found in cooling towers can be attributed to the biological source as discussed or scaling or deposits of minerals onto surfaces. The corrosion can cause equipment failure, loss of efficiency of heat transfer because of heat exchanger fouling, and loss of structural integrity.
The antifouling measures adopted to control biofouling depend on the type of cooling system and fouling organisms. Protecting the interior and exterior of the tower will help prevent corrosion and leaks. An epoxy coating to seal and eliminate leaks will extend the life of your equipment.
Resources:
Cooling Towers: Understanding Key Components of Cooling Towers and How to Improve Water Efficiency
 source: Biofouling: lessons from nature
source: Biofouling: lessons from nature
Key Takeaways:
Process: Noticeable microorganisms appear inside the cooling tower
Problem: The reduction in heat transfer efficiency, reduces equipment availability, expensive downtime, and outages, and threatens the structural integrity of the equipment with corrosion
Prevention: Monitoring and treatment strategies to address and fix biofouling
3. Biofouling and its Impact on People and the Environment
Biofouling occurs in a wide range of industrial processes. The underlying problem is the same for all, biofilms, which is the collection of one or more types of microorganisms that grow on surfaces. Biofilms can harbor populations of disease-causing bacteria such as Legionella and listeria.
Another referred term is Microbially Influenced Corrosion (MIC). Many industries are affected by MIC, ranging from chemical processing industries, nuclear power generation, water treatment, and more.
Biofouling corrodes pipes and contaminates the wastewater they are transporting.
Resources:
Biofouling Control Options for Cooling Systems
4. How an Epoxy Coating System Prevented Acid Rain and Salt Against Chemical and Atmospheric Corrosion (Case Study)
Location: Port Neches, TX
Problem: A global manufacturer of differentiated chemicals was experiencing issues with their pipes in specific areas of the facility due to caustic soda (acid rain) coming from their cooling towers. Coupled with their proximity to the Gulf Coast, salt (electrolyte) was introduced, creating the perfect storm for corrosion to form.
Solution: The chemical resistant nature of the ChemLINE® 784 coating system was an ideal fit to protect their current assets against chemical and atmospheric corrosion.
Request a coating recommendation.
Conclusion






